This press release first appeared in the Green Citizens’ Action Alliance on 17/08/2023, and the key points are translated into English and republished here.
· Only 7% (128) of Taiwanese listed companies have committed to net-zero by 2050, which slightly increased from 3% last year.
· Although 18% (334) of listed companies have interim targets for GHG reduction, they do not make pledges to get to net-zero emission.
· 75% (1300+) of listed companies have not set GHG reduction targets nor mentioned any future plan to reduce GHG emissions.
· In Taiwan, there are 293 hard-to-abate companies with annual emissions more than 25 kilotons of CO2e, [1] but merely 8% (24) of them have committed to reach net-zero target by mid-century.
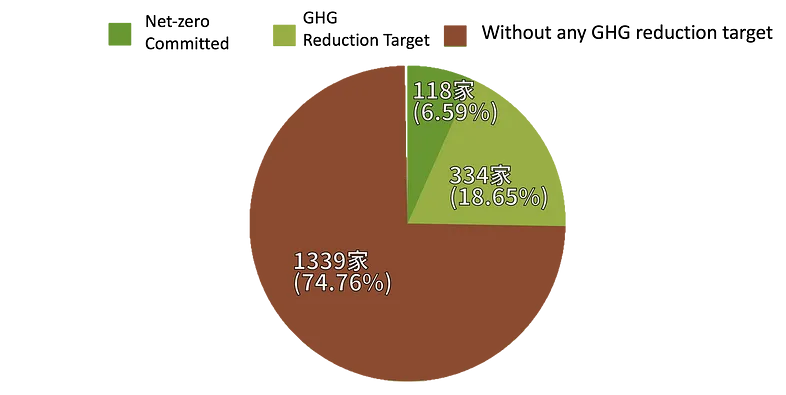
The Taiwanese government has already committed to reach net-zero emissions by 2050 since 2021. Earlier this year, the amendment of “Climate Change Response Act” was finished; relevant policies and “12 Key Strategies for net-zero transition” are also being implemented by the government entities at all levels. To track climate progress of Taiwanese corporates, the Green Citizens’ Action Alliance (GCAA) collected and analyzed Taiwanese listed companies’ latest public disclosure of climate-related information on the reporting system of governmental website [2], however, the findings showed that most companies do not on the track of 1.5°C climate goal as they have not set GHG reduction targets and/or concrete strategies; some of them even have not finished GHG accounting.
GCAA also investigated the listed companies that are required to report their GHG emissions (scope1 and 2) to the authority,[3] and found that around 40% (32) of them do not have any GHG reduction target. It seems that Taiwanese government needs to develop more effective and comprehensive climate policies to push those unprepared companies to take further climate action, otherwise they may slow down the overall net-zero timeline, and then Taiwan will fail to achieve 2050 climate pledges.
In view of this, in mid-August, environmental NGOs of the Taiwan Climate Action Network (TCAN) held a press conference and made four requests to call on Taiwanese authority and listed companies to act:
1. Taiwan’s net-zero strategies should be “12+1,” i.e., Ministry of Economic Affairs should come up with a comprehensive industrial decarbonization plan based on the existing 12 key strategies, since current strategies do not have a coherent action plan to decarbonize industrial sector nor innovative policy tools to encourage hard-to-abate industries to accelerate adoption of low-carbon technologies. Therefore, relevant ministry (Ministry of Environment, Ministry of Economic Affairs, and Financial Supervisory Commission at least) should strengthen and integrate various policy tools and explain how to implement them to guide industrial net-zero transformation.
2. The Financial Supervisory Commission should revise the requirements regarding corporate climate-related information disclosure based on the recommendations from United Nations’ Integrity Matter report. Moreover, FSC should supervise the quality of sustainability reporting so that the stakeholders can access accurate corporate climate-related information.
3. The authority should establish an appropriate monitoring mechanism (e.g., EU’s “Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive”) to make sure that companies’ climate transition progress aligns with 2050 net-zero timeline.
4. Large carbon emitters should further develop corporate climate transition plans, not just remaining 2050 net-zero commitment and/or short-term unambitious climate target. Besides, when the Ministry of Environment charge specific companies carbon fees with preferential rate in the future, the government officials should consider the corporates’ climate transition plans to ensure their business strategies and corporate governance are consistent with net-zero pathway.
Note:
[1] Hard-to-abate sectors include steel, cement, chemicals, trucking, shipping, and aviation industries, currently, their emissions (scope1& 2) account for around 40% of Taiwan’s emissions.
[2] Taiwanese law has required that certain industries and large listed companies have to report critical sustainability information per year on specific website (MOPS) since 2014, and the content for reporting is often revised to catch up with global sustainability standards (e.g. GRI, TCFD, ISSB.) Currently, the number of companies that need to report sustainability information is around 1800.
[3] From 2016, Taiwanese law requires that major emitters (energy-intensive sectors and the companies with annual emissions more than 25 kilotons of CO2e) must disclose their GHG scope1 and 2 emissions verified by independent third party on website of Ministry of Environment. Currently, the number of companies that need to report GHG emissions is around 280.




